A series circuit looks like a single pathway where electrical current flows uniformly through all components. Each part, like resistors and voltage sources, connects in a line, creating one continuous loop. The current remains the same throughout, while voltage drops vary based on the resistance of each component. If one part fails, the entire circuit stops working. Want to know more about the behavior and applications of series circuits? There’s plenty to explore!
Key Takeaways
- A series circuit consists of components connected in a single linear pathway for current flow, with no branches or alternative routes.
- Components like batteries and resistors are arranged in a sequence, illustrating a direct route for electricity.
- Current flows uniformly through all components, ensuring the same current passes through each element in the circuit.
- The circuit diagram typically shows clear entry and exit points for current, emphasizing its continuous loop design.
- Voltage drops across each component vary based on resistance, with total voltage drop equaling the supply voltage.

REXQualis Electronics Basic Kit w/Power Supply Module, Breadboard, Jumper Wire, LED,Resistor, comes with more than 300pcs sensors and components for fun and simple electronic projects.
Highest Cost Components Kit: It comes with more than 300pcs sensors and components for fun and simple electronic…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Definition of a Series Circuit
A series circuit, which consists of a single, continuous path, allows electric current to flow through each component one after the other. In this arrangement, all components share the same current, ensuring that the current remains constant throughout. However, as you add more components, the overall resistance increases, reducing the total current flowing through the circuit. One key aspect to remember is that if any component fails, the entire circuit stops functioning. This simplicity makes series circuits easy to construct and understand, but it also means there’s no alternative pathway for current. Unlike parallel circuits, in series, voltage varies across components, acting as a voltage divider based on each component’s resistance or capacitance. Additionally, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances in a series circuit, which affects the overall performance of the circuit. In terms of electrical concepts, understanding voltage division is essential for analyzing how voltage distributes across components in a series circuit. Furthermore, the basic principles behind primitive weapons can inspire creative solutions to survival challenges, showcasing the importance of resourcefulness in various scenarios. Moreover, the performance of electronic systems can be significantly enhanced by utilizing automation’s role in data analysis and decision-making processes. Curiosity can also play a crucial role in exploring innovative ways to improve circuit designs and functionalities.

BOJACK 1000 Pcs 25 Values Resistor Kit 1 Ohm-1M Ohm with 5% 1/4W Carbon Film Resistors Assortment
BOJACK resistor assortment kit contains 1000pcs resistors with variety values. Enough quantity for your DIY project and experiments
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Components of a Series Circuit
Understanding the components of a series circuit is key to grasping how it operates. The main parts include resistors, loads, voltage sources, switches, and wiring.
Resistors slow down current and increase overall resistance, affecting the voltage drop based on their values. Loads, like light bulbs or motors, convert electrical energy into other forms and are connected end-to-end, meaning if one fails, the whole circuit stops working. This is because in a series circuit, if one component fails, the entire circuit becomes open. Proper tax planning can ensure that withdrawals from retirement accounts do not negatively impact the circuit of your finances. Additionally, diversification of financial assets can help mitigate risks similar to how resistors manage electrical flow. It’s important to consider that long-term financial planning can also provide stability in managing overall expenses. The interconnectedness of components in a series circuit mirrors the importance of emotional resilience in maintaining overall well-being.
Voltage sources, such as batteries, provide the necessary electrical energy, and their total voltage drives the current through the circuit. Switches control the flow of current, while protective devices ensure safety.
Lastly, wiring connects everything, creating a continuous path, so secure connections are crucial for proper circuit function.

EUDAX Fruit Battery Science Experiment Kit with Electronic Clock and RGB LED for DIY Home Teaching Equipment, School Science Project, Education Subject
Package Includes: 4 pieces copper sheet, 4 pieces zinc sheet,1 piece Electronic clock,2 pieces RGB LED,4 pieces Wire,…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Series Circuit Diagram

Series circuit diagrams visually represent how components connect in a single pathway for current flow. In these diagrams, components like batteries and resistors are arranged linearly, connected end-to-end. You’ll typically see the battery at one end, with wires depicted as straight or slightly angled lines connecting each component. Each component features clear entry and exit points for current flow, highlighting the simplicity of the circuit. There are no branches or alternative routes, forming a single loop. If you’re creating a diagram, start with the power source, add components in sequence, and consider using arrows to indicate current direction. These diagrams are essential for understanding circuit functionality and analyzing interactions between components, as they illustrate how series circuits maintain a constant current flow through all components. Furthermore, in a series circuit, the total resistance increases with each added component, similar to how portable camping toilets provide added convenience in outdoor settings. Additionally, just like how air purifiers rely on a consistent airflow to function effectively, series circuits depend on a steady current to power each component. Proper understanding of circuit components can greatly enhance your ability to design effective circuits. It’s important to note that zoning laws can impact where you might set up a tiny home, much like how circuit components must be placed in specific configurations to ensure functionality.

EISCO Simple Circuit Kit – Electricity Kit for Building Basic, Parallel & Series Circuits – Includes Batteries, Wire, Bulbs, Knife Switch, Holders & Experiment Guide
HANDS ON LEARNING || This hands on learning kit is perfect for introducing students to the basics of…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Behavior of Series Circuits
When you connect components in a series circuit, their behavior is intrinsically linked due to the single pathway for current flow. Current flows uniformly through all components, meaning each one experiences the same amount of current. If you add more components, total resistance increases, which reduces the current. Conversely, increasing the power source voltage can boost current flow. Each component’s voltage drop relates directly to its resistance, and the total drop equals the supply voltage. This relationship highlights that total resistance in series circuits is the sum of individual resistances, impacting overall current flow. Additionally, understanding heat pumps and indoor air quality can help illustrate how systems with interconnected components can enhance performance. Furthermore, just as in energy efficiency ratings, optimizing each component’s performance in a series circuit can lead to improved overall efficiency. This concept mirrors how predictive modeling can help identify at-risk students in educational settings by analyzing the interconnected data of their performance. Moreover, the performance of a series circuit can be influenced by the energy savings achieved through efficient component design and material selection.
Characteristics of Series Circuits
Because components are connected end-to-end in a series circuit, the flow of electricity is straightforward and uniform. You’ll notice that the current flowing through each component is the same, which means you can predict its behavior easily. However, voltage drops vary depending on each component’s resistance or capacitance. The total resistance equals the sum of individual resistances, and the total voltage is the sum of individual voltage drops. If one component fails, it halts the current flow entirely, affecting the entire circuit. Changing the resistance of one component impacts the whole setup. This simplicity makes series circuits easier to analyze than more complex configurations, allowing for effective voltage division in your designs. Additionally, the total resistance in a series circuit increases with each added component, which can significantly affect overall current flow. Understanding current flow is essential for designing efficient electronic devices, especially as it relates to energy efficiency ratings which can influence circuit performance. Furthermore, the concept of sustainable fashion parallels this, as both emphasize the importance of cohesive design and the impact of each element on the overall system. Moreover, understanding low light office plants can inspire innovative ways to integrate nature into electronic design, enhancing overall well-being in workspaces.
Applications of Series Circuits
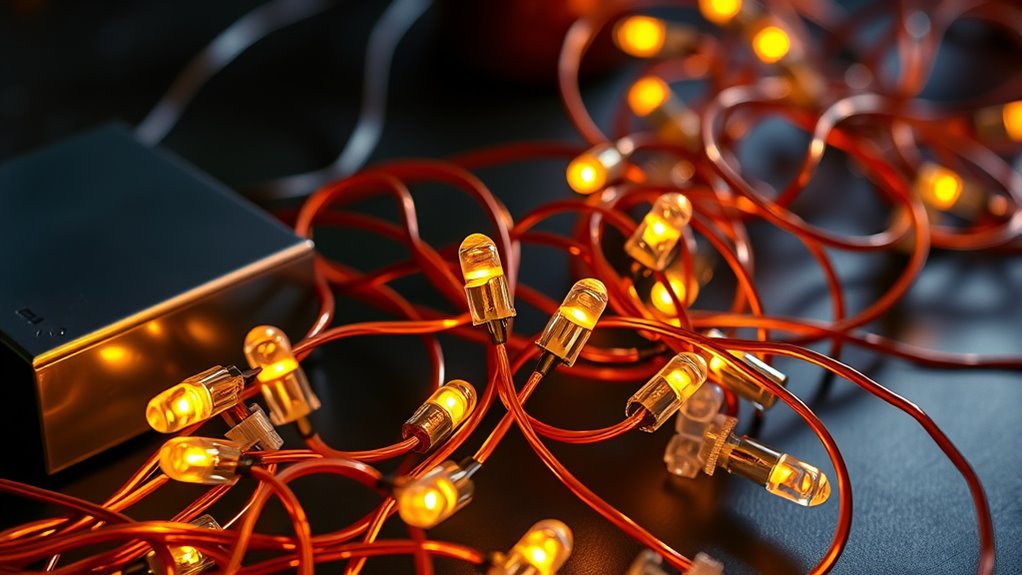

Understanding the characteristics of series circuits helps highlight their practical uses in various applications.
You’ll find series circuits in holiday lights, connecting multiple bulbs in a single path. In battery packs, cells are wired in series to boost voltage, which powers tools and electronics. The same current flows through all components in a series circuit, ensuring consistent performance across devices. Additionally, high voltage systems often utilize series circuits to enhance efficiency and functionality. Mammography aims to detect breast cancer early is an important principle that underscores the need for precision in applications requiring reliability. Proper planning can help avoid costly errors in circuit design, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Implementing small mistakes in circuit design can lead to significant issues, making awareness essential for successful applications.
Older lighting systems in trains also relied on this design for simplicity and cost-effectiveness. In your home, some appliances and garden lights utilize series connections for ease of use.
Even in industrial settings, series circuits power tools and electric vehicles by linking batteries for higher voltage.
From DIY projects to medical equipment, series circuits remain vital for customizing voltage and ensuring reliable performance in diverse applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens if I Add More Components to a Series Circuit?
When you add more components to a series circuit, you increase the total resistance. This means the overall current flowing through the circuit decreases, as it has to pass through each additional resistor.
Each component will also experience a different voltage drop based on its resistance. If one component fails, the entire circuit stops functioning, so it’s crucial to consider how many components you want to include.
Can I Use Series Circuits for High-Power Applications?
You can definitely use series circuits for high-power applications, but be aware of their limitations.
While they can increase voltage and simplify design, each component must handle the same current, which can lead to higher costs and complexity.
If one component fails, the whole circuit stops working.
So, weigh the benefits against potential risks, especially in safety-critical situations where reliability is paramount.
Knowing these factors will help you make informed decisions.
How Do I Calculate Total Voltage in a Series Circuit?
To calculate total voltage in a series circuit, you need to add up the voltage drops across each component.
Use Ohm’s law (V = IR) for each resistor to find these drops. Once you’ve got the voltage drops, sum them up to get the total voltage.
Are Series Circuits Safe for Household Wiring?
When it comes to safety, series circuits can be a double-edged sword.
They’re generally not ideal for household wiring because if one device fails, everything goes dark. You wouldn’t want to be left in the lurch!
While series circuits can be used in specific applications like holiday lights, they pose risks if not properly grounded.
For everyday use, parallel circuits are safer and more reliable, allowing devices to function independently.
How Do Series Circuits Compare to Parallel Circuits?
When you compare series circuits to parallel circuits, you’ll notice key differences.
In a series circuit, all components share a single path, so if one fails, the whole circuit stops working. Conversely, parallel circuits offer multiple paths, allowing components to function independently. This makes parallel circuits more reliable for everyday use.
While series circuits are simpler to wire, they can’t match the flexibility and performance of parallel circuits in most applications.
Conclusion
In summary, a series circuit connects components in a single path, allowing current to flow through each one sequentially. Did you know that in a series circuit, if one component fails, the entire circuit stops working? This highlights the importance of each part in maintaining functionality. Understanding series circuits can help you grasp the fundamentals of electrical systems, making it easier to troubleshoot and design your own projects. So, get out there and explore the world of circuits!